Redirecting domains greatly enhances SEO and user experience by seamlessly guiding visitors from an old domain to a new domain. To set up a domain redirect, you need to configure your domain settings to forward users from one URL to another using HTTP status codes like 301 for permanent redirects or 302 for temporary redirects. This is essential for maintaining SEO rankings and guaranteeing users reach the correct website.
You can set up redirects through your domain registrar’s control panel, web hosting service, DNS settings, or using WordPress plugins. Each method involves specifying the source URL, destination URL, and redirect type. After setting up the redirect, test it across different browsers to confirm functionality. You will learn more about the specific steps and considerations involved.
Table of Contents
What is Domain Redirect?
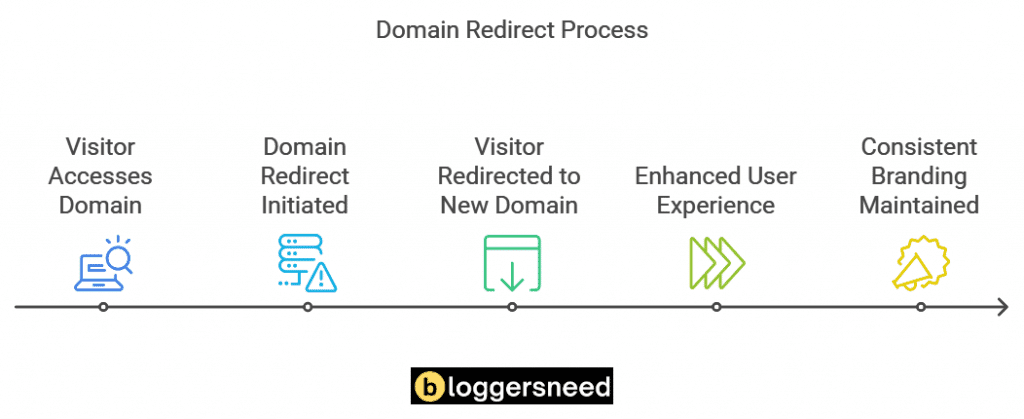
A domain redirect is a technique used to automatically forward users and search engines from one URL to another, ensuring that visitors and search engine crawlers are directed to the correct page when a webpage is moved to a new address or when a domain name is changed. This process involves configuring a URL on one website so that when someone clicks on it, they are directed to a different site.
This method helps direct visitors to the correct website, maintaining search engine optimization (SEO) and preventing duplicate content.
For example, if a user types googl.com, Google redirects them to google.com to guarantee users reach the right site.
What Are the Benefits of Domain Redirects?
Domain redirects offer several key benefits that can greatly enhance your online presence and user experience.
You can use domain redirects to improve your SEO advantages by preserving the ranking and link equity of your old URLs. This guarantees that your website remains visible in search engine results, driving more organic traffic.
Domain redirects also enhance user experience by seamlessly directing visitors to the correct pages, reducing the likelihood of encountering 404 errors.
In addition, they assist in traffic management by allowing you to redirect users to temporary maintenance pages or queuing subdomains during high traffic periods.
Additionally, domain redirects help maintain brand consistency by ensuring all related domains point to your main site, and they enable analytics tracking to monitor user behavior effectively.
What Are the Drawbacks of Domain Redirects?
While domain redirects offer several key benefits for enhancing your online presence and user experience, they also come with some drawbacks.
Redirect pitfalls can negatively impact your user experience if not implemented correctly. For instance, excessive redirect chains can slow page load times and frustrate users.
Furthermore, SEO implications can arise if redirects aren’t set up properly, potentially leading to a loss of PageRank and traffic.
Traffic loss is another concern, as incorrect redirects can result in users landing on irrelevant pages, increasing bounce rates.
What Steps Are Involved in Setting Up a Domain Redirect?
When you need to redirect a domain to another, you’ll typically start by accessing your domain registrar or web hosting account.
To set up a domain redirect, follow these steps.
- Access Your Domain Registrar or Web Hosting Account: Log in to your domain registrar or web hosting account to manage your domain settings.
- Navigate to Domain Management: Find the domain management section and select the domain you want to redirect.
- Set Up the Redirect: Enter the destination URL. Choose the redirect type (301 permanent or 302 temporary). Save the changes.
- Test the Redirect: Confirm the redirect works by entering the original domain in a web browser.
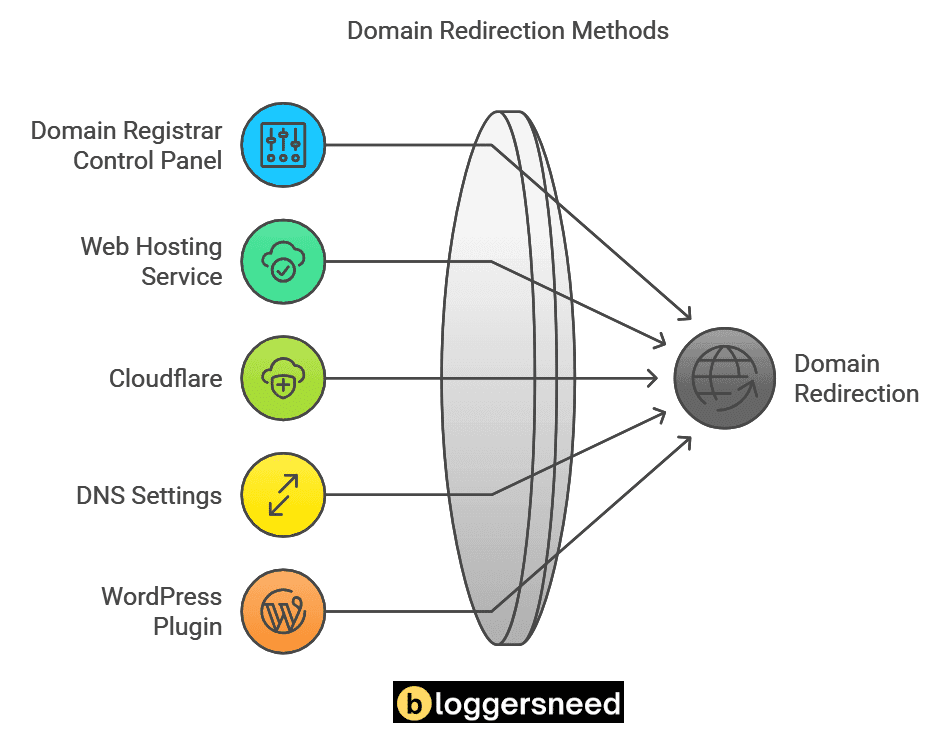
What Are the Different Methods of Domain Redirection?
To set up a domain redirect, you have 5 options such as you can use your domain registrar’s control panel, your web hosting service, Cloudflare, DNS settings, or even a WordPress plugin to implement the redirect.
Each method has its own set of instructions and considerations, such as choosing between permanent (301) and temporary (302) redirects, which can affect your site’s SEO and user experience.
1. Using Domain Registrar Control Panel
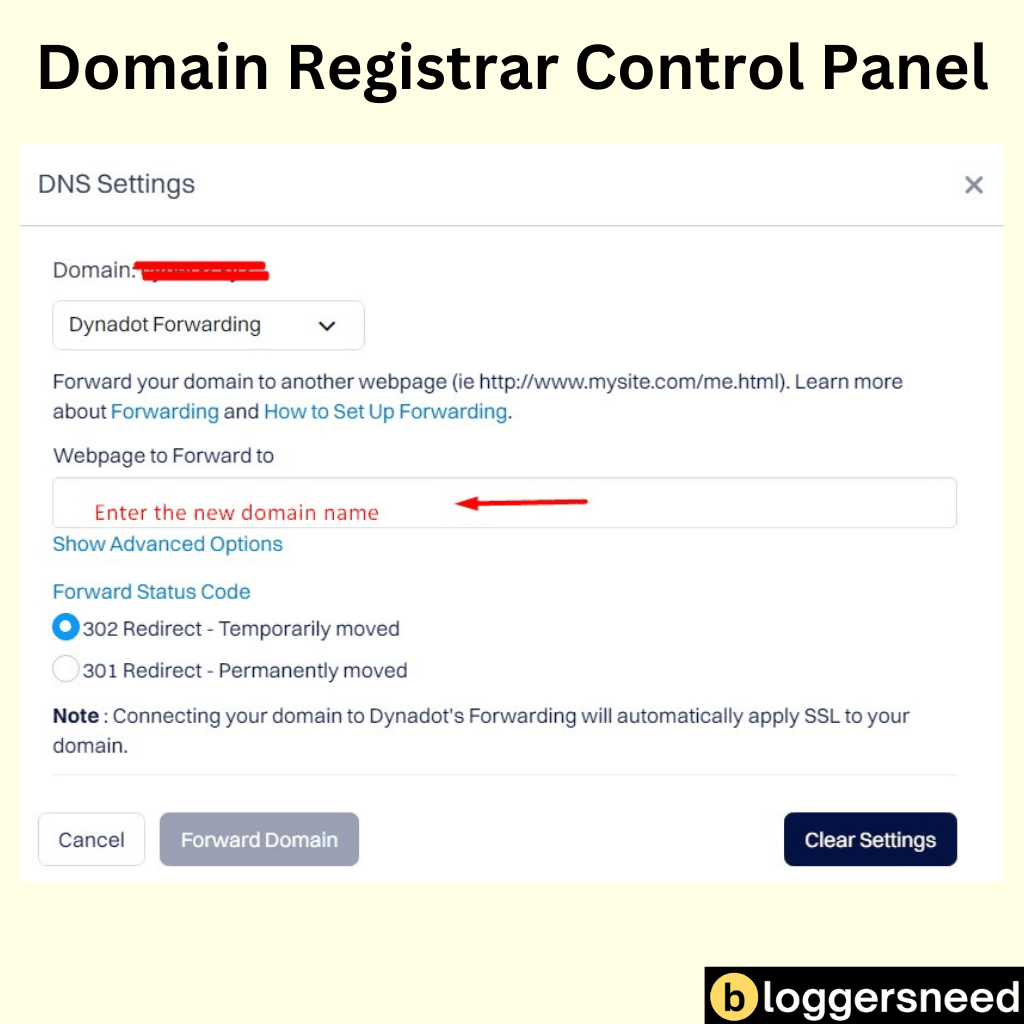
Using your domain registrar’s control panel is a straightforward method for setting up domain redirects. You can manage DNS settings, including name servers, and update WHOIS information through the control panel.
Most domain registrars offer a user-friendly interface with features like DNS management, domain transfer, and redirect types. For example, Dynadot control panel allows you to manage your domain, update DNS settings, and update WHOIS information.
To access the control panel, you’ll need your domain name and password. Once logged in, you can set up redirects, manage DNS records, and update your domain’s settings.
This method provides a perfect user experience, allowing you to easily manage your domain and redirects in one place.
2. Using Web Hosting Service
To set up a domain redirect using your web hosting service, you can utilize tools like cPanel or modify the .htaccess file.
In cPanel, you can find the Redirects icon under the Domains section, where you can choose the type of redirect, such as a 301 permanent redirect or a 302 temporary redirect, and specify the destination URL.
cPanel
Setting up a domain redirect in cPanel is a straightforward process that allows you to forward visitors from one domain or page to another.
cPanel features a Redirects tool under the Domains section, where you choose the type of redirect (Permanent or Temporary) and specify the URL to redirect to.
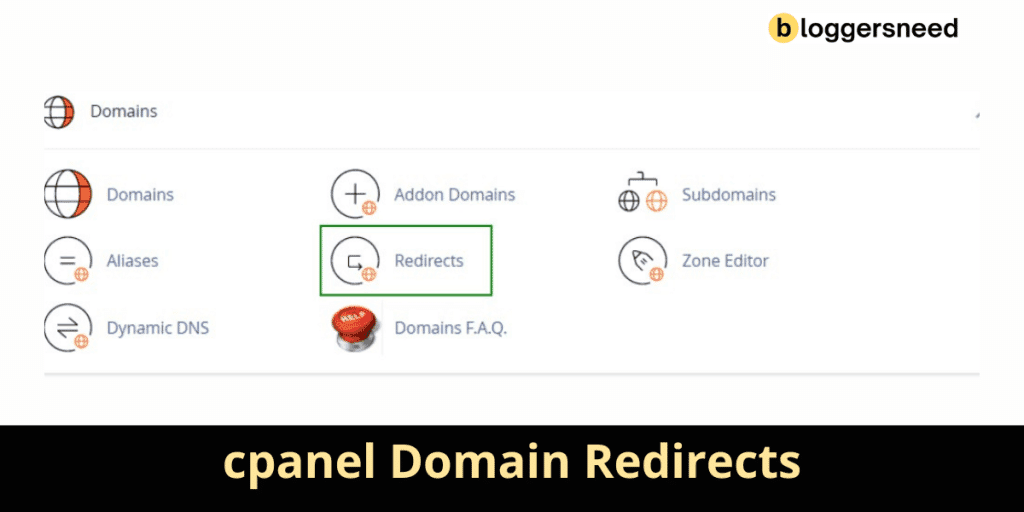
You can also select options for handling www redirection and enabling Wild Card Redirect for directories.
htaccess Redirect
Domain redirection is an essential aspect of managing web traffic and SEO.
To set up a domain redirect using .htaccess, you’ll need to edit the .htaccess file in your website’s root directory.
# Enable the RewriteEngine
RewriteEngine On
# Redirect from old-domain.com to new-domain.com
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^old-domain\.com [NC]
RewriteRule ^(.*)$ https://new-domain.com/$1 [L,R=301]Add the redirect rule, specifying the old and new URLs. For example, ‘Redirect 301 /old-page/ https://www.yourdomain.com/new-page/’.
This method guarantees a permanent redirect status, preserving SEO implications.
3. Using Cloudflare
Cloudflare offers multiple methods for domain redirection, each tailored to specific use cases.
To set up a domain redirect using Cloudflare, you need to configure your DNS settings and create a redirect rule. First, verify your domain is set up in Cloudflare with DNS management enabled.
Then, create two A records, one for the root and one for the WWW subdomain, both pointing to a special IP address like 192.0.2.1 and with the “Proxied” status on.
Next, go to the “Rules” section and create a new redirect rule. Choose “All incoming requests,” select “Static” and “301 Permanent Redirect,” and enter the destination URL.
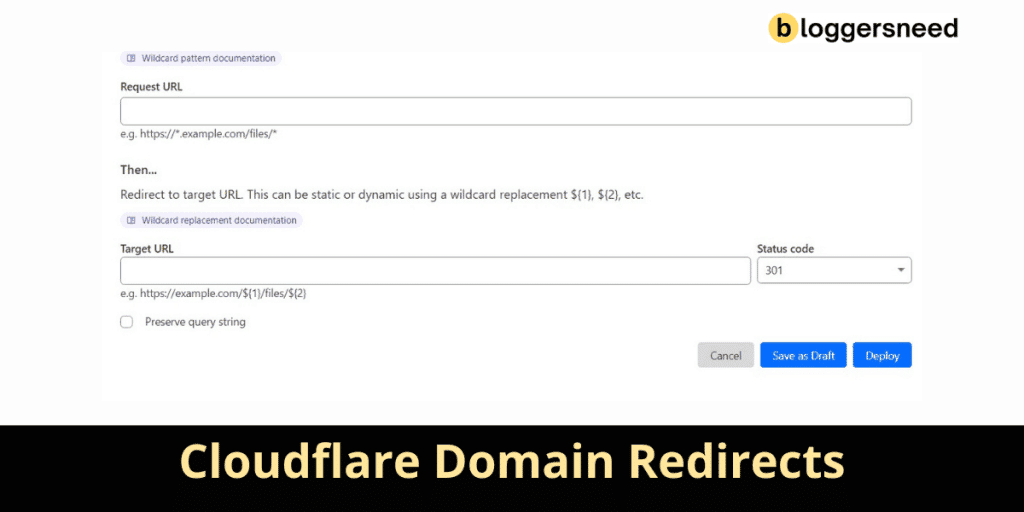
Save and deploy the rule to activate the redirect.
4. Using DNS Settings
When setting up domain redirection, you can use various DNS settings to achieve this.
To start, access your DNS provider’s control panel or management interface and locate the DNS Management section. Here, you can add a new record by selecting the appropriate record type, such as A (Address) or CNAME.
For an A record, enter the hostname or subdomain you want to redirect and set the IP address of the destination server. For a CNAME record, enter the hostname or subdomain and the destination domain or hostname.
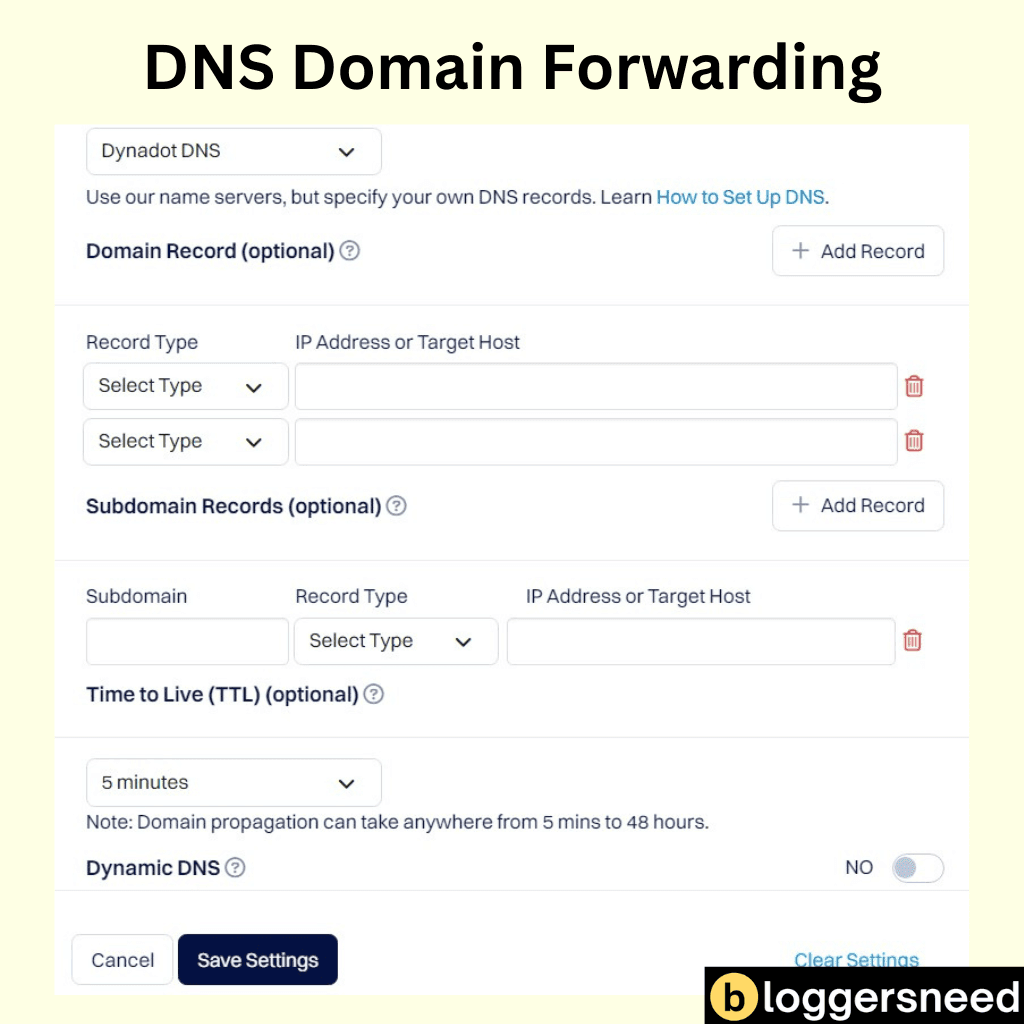
Save the changes and test the redirect to confirm it works correctly. Effective domain configuration and traffic handling are vital for successful URL forwarding.
Always verify the redirect methods and clear your DNS cache if issues arise.
5. Using WordPress Plugin
How do you handle domain redirection when you’re using a Content Management System (CMS) like WordPress?
You can use WordPress plugins to manage domain redirection effectively. These plugins offer various features such as creating temporary and permanent redirects (301, 302, 307), tracking 404 errors, and ensuring seamless user experiences.
For ideal SEO implications, plugins like Redirection, SEO Redirection, and 301 Redirects provide extensive solutions.
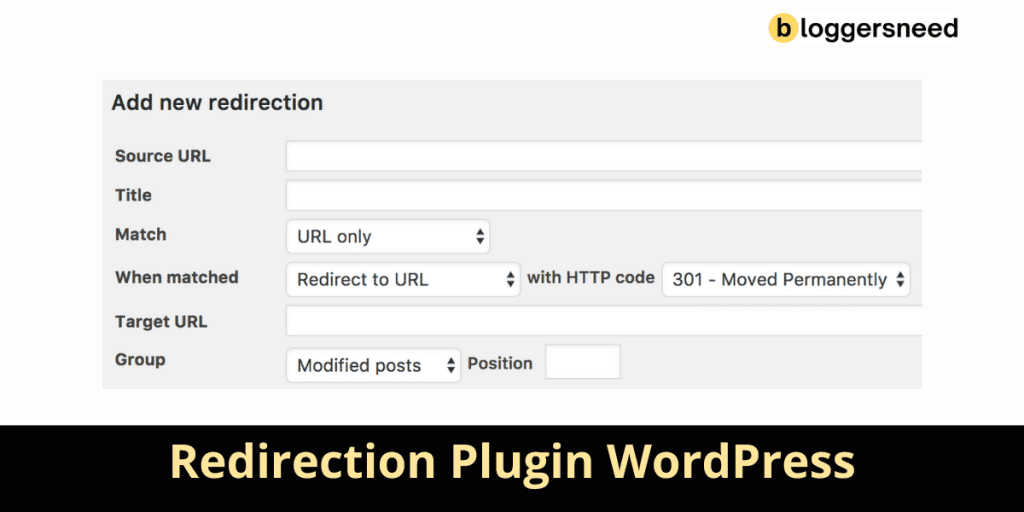
When choosing a plugin, consider factors such as plugin compatibility with your WordPress version and the types of redirects you need.
For instance, Redirection supports automatic creation of 301 redirects when post or page URLs change, ensuring minimal impact on SEO and user experience.
What Are the Types of Redirects?
When setting up a domain redirect, you need to understand the different types of redirects available.
The two primary types are the 301 Permanent Redirect and the 302 Temporary Redirect.
The 301 redirect is ideal for permanent changes, such as moving your website to a new domain, while the 302 redirect is suitable for temporary changes, like website maintenance.
1. 301 Permanent Redirect
Permanent redirects are an essential tool for website management, guaranteeing that users and search engines are directed to the correct location when a webpage or resource has been permanently moved.
You should use a 301 redirect for this purpose, as it passes full link equity (ranking power) to the redirected page. This setup helps maintain SEO implications by signaling a permanent change to search engines.
For browser compatibility, guarantee server-side implementation to avoid issues with JavaScript redirects. Be cautious of redirect loops, which can harm user experience and negatively impact analytics tracking.
For instance, if you move a page from http://example.com/old-page to http://example.com/new-page, use a 301 redirect to preserve backlinks and maintain SEO rankings.
This approach guarantees a smooth shift for both users and search engines.
2. 302 Temporary Redirect
Temporary redirects, denoted by the 302 status code, serve a different purpose than their permanent counterparts. They’re used when you need to temporarily redirect traffic from one URL to another, such as during site maintenance or updates.
Temporary redirect types include 302 redirects and 307 redirects. The 302 redirect is typically used for GET requests, while the 307 redirect is used for non-GET requests to preserve the original request method.
Temporary redirect examples include redirecting users to a different page based on their location or language preferences, or temporarily redirecting traffic during site updates.
When using temporary redirects, consider the impact on SEO. Temporary redirects don’t transfer SEO value, so they should be used sparingly and only when necessary.
However, they can provide benefits such as preserving user experience during site maintenance. Always delete the redirect when it’s no longer needed to avoid any negative effects on your SEO.
How Can I Confirm That My Redirect Is Working Across All Major Web Browsers?
To confirm that your redirect is working across all major web browsers, you need to manually inspect the link in each browser or use built-in developer tools. Open the URL in different browsers like Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge, and observe if the URL changes or any notification indicates a redirect.
Alternatively, use the browser’s developer tools to inspect network activity and identify HTTP status codes in the 300 range, such as 301 or 302, which indicate a redirect.
You can also use online redirect testing tools like Redirect Checker or Sitechecker to analyze the redirect path.
Additionally, test the redirect on mobile browsers and check for caching issues to guarantee a smooth user experience.
What Are the Frequently Asked Question About Domain Forwarding?
As you set up your domain redirect, several frequently asked questions may arise.
You may think if setting a domain to redirect deletes your website files, or what type of redirect is created when setting this up through your hosting panel.
Additionally, you might question whether redirecting works for both the www and non-www versions of your site, and if the redirect changes your MX records.
Do I Need Hosting to Redirect a Domain?
Do you really need hosting to redirect a domain? No, you don’t.
You can set up a redirect using your domain registrar’s settings or via DNS. Some registrars, like NameCheap, allow 301 redirects without hosting.
You can also use URL forwarding, which doesn’t require hosting. Just make sure you choose the right redirect type (301 or 302) for your needs.
Does Domain Forwarding Cost?
No, Domain forwarding is generally a free service offered by most domain registrars.
However, some registrars charge a yearly fee, such as Network Solutions ($12.99/year/site) and Register.com ($12.00/year/site).
In contrast, providers like Openprovider, Google Domains, and Porkbun offer free domain forwarding.
Always compare pricing plans and consider domain management fees when choosing a registrar for domain redirect services.
Is Domain Forwarding Bad for SEO?
Domain forwarding can have both positive and negative impacts on your website’s SEO, depending on how it’s implemented.
Properly configured domain forwarding helps maintain consistent branding, simplifies URLs, and can aid SEO by ensuring search engines index your site under a single domain.
However, incorrect setup can lead to content duplication issues and lower page rank.
Why My Domain Redirecting Multiple Times?
When your domain redirects multiple times, it typically indicates a misconfiguration in your website’s settings or server configuration.
This can lead to redirect loops or chains, often caused by incorrect HTTPS settings, misconfigured WordPress plugins, or issues with browser caching.
These errors can have SEO implications and should be addressed promptly to avoid negatively impacting your site’s accessibility and search engine rankings.
Can I Redirect My Domain to Another Website?
Yes, you can redirect your domain to another website by configuring your domain’s DNS settings to point to the IP address or URL of the website you want to redirect to, which allows visitors to access the content of the other website when they visit your domain.
How to Stop Domain Redirect?
To stop a domain redirect, you need to access the control panel of your domain hosting service.
Log in to your cPanel account and navigate to the “Domains” section. Click on “Redirects” and scroll down to the “Current Redirects” section.
Locate the domain redirect you want to remove and click on the “Remove” icon. Confirm by clicking “Remove Redirect” again.
Additionally, you may need to check for redirect troubleshooting issues, such as browser cache and redirect loops, which can be resolved by clearing browser cache or adjusting server configuration.
Effective domain management involves regularly reviewing and updating redirects to prevent unwanted redirections.
Affiliate Disclosure: Some of the links in this post are affiliate links, which means I may earn a small commission if you make a purchase through those links. This comes at no extra cost to you. Thank you for your support!
