
On-Page SEO serves as the foundation for higher search rankings and long-term content visibility.
At BloggersNeed, we write all our articles by following On-Page SEO techniques.
It is my favorite optimization technique to rank content on search engines.
When done right, on-page SEO accounts for 80% of your effort, leaving only 20% for off-page SEO and link building.
By strategically optimizing content, internal links, entities, and user experience signals, you can rank without relying heavily on backlinks.
In this guide, I’ll break down step-by-step On-Page SEO strategies, from keyword structuring to semantic optimization, with real-world examples of what works and what doesn’t.
Let’s dive in.
Table of Contents
What is On-Page SEO?
On-page SEO is the process of optimizing individual web pages to rank higher in search engines through content and HTML source code optimization.
How to Do On-Page SEO?
To do on-page SEO, you need to follow proper writing techniques, such as choosing the focus keyword, LSI and secondary keywords, creating a proper title and meta description, implementing H2-H6 for logical content hierarchy, maintaining keyword density, optimizing image tags, using the proper schema type, adding internal links with the right anchor text, and correctly implementing bold, italics, and lists.
Additionally, ensure a clean and concise URL structure with the focus keyword, optimize for mobile-friendliness, improve page load speed, maintain content readability, ensure sufficient content length, and consider user engagement signals like time on page and bounce rate.
To make the process simpler for beginners, we’ve compiled 21 steps to implement effective on-page SEO and enhance your website’s visibility and search engine rankings.
Step 1: Keyword Research & Mapping
- Research primary and secondary keywords using tools like Google Keyword Planner
- Map keywords to specific pages based on search intent
- Correct: “best coffee makers” → dedicated buying guide page
- Incorrect: Stuffing multiple unrelated keywords on one page
Step 2: Title Tag Optimization
- Include primary keyword near the beginning
- Keep length between 50-60 characters
- Add compelling call-to-action
- Correct: “Best Coffee Makers 2024: Top 10 Ranked & Reviewed”
- Incorrect: “Coffee Makers – Buy Coffee Makers – Coffee Machine Reviews – Best Prices”
Step 3: Meta Description Creation
- Write unique 150-160 character descriptions
- Include primary keyword naturally
- Add clear value proposition
- Correct: “Discover the top-rated coffee makers of 2024. Compare features, prices, and expert reviews to find your perfect brew companion.”
- Incorrect: “Coffee makers coffee machines best coffee makers cheap coffee makers buy coffee makers online coffee maker reviews coffee maker prices.”
Step 4: Header Structure
- Use H1 for main title (only one per page)
- Implement H2-H6 for logical content hierarchy
- Include relevant keywords naturally
- Correct:
H1: Best Coffee Makers 2024
H2: Top-Rated Drip Coffee Makers
H3: Budget-Friendly Options - Incorrect:
Multiple H1 tags
Random header hierarchy
Keyword-stuffed headers
Step 5: Content Optimization
- Write comprehensive, original content
- Maintain 2-3% keyword density
- Include LSI keywords and related terms
- Structure content with short paragraphs
- Add bullet points and numbered lists
- Correct: Natural integration of keywords with valuable information
- Incorrect: Repetitive keywords without meaningful context
Continue steps 6-21 following same format for:
- Image optimization
- URL structure
- Internal linking
- Schema markup
- Mobile optimization
- Page speed
- User experience elements
- Content freshness
- Social signals
- Entity relationships
- Semantic relevance
- Technical elements
- Core Web Vitals
- User behavior metrics
- Content depth
- Multimedia integration
1. Identify the Focus Keyword and Map Entity Relationships
Focus keyword identification is the process of selecting primary search terms for content optimization, while entity mapping establishes semantic connections between related concepts to build topical authority.
To write an article about any topic, identify focus keyword used by internet users, selecting those with minimal search volume.
I follow the exact on-page SEO steps for finding focus keywords to write article.
To effectively conduct keyword research, utilize tools such as Google Keyword Planner or other reliable keyword research platforms to identify low-competition keywords.
- Analyze search volume and competition
- Select terms matching user intent and business goals
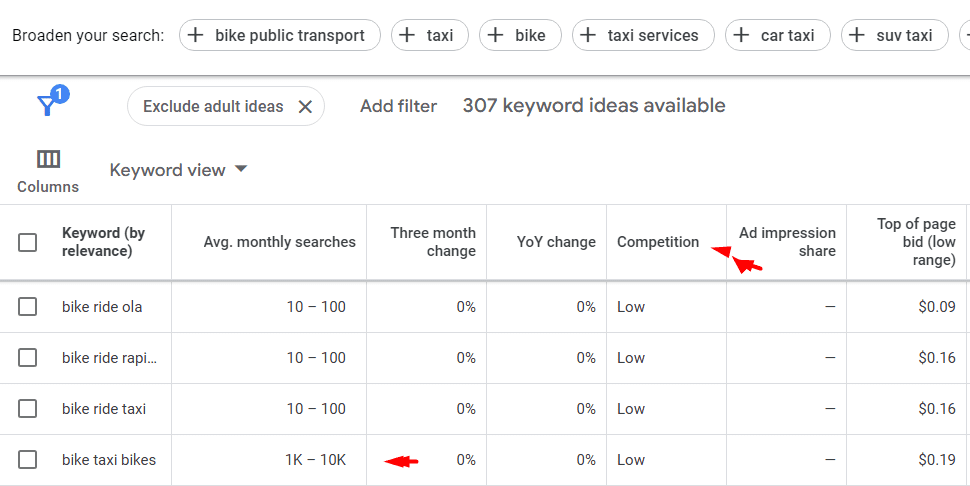
Identify semantic variations and related terms of main focus keyword.
- List synonyms and long-tail variations
- Include common industry phrases and alternative expressions
Create keyword clusters
- Group thematically related terms
- Organize by search intent and topic relevance
Map entity relationships
- Draw connections between main topics and subtopics
- Link attributes and characteristics to core concepts
- Document hierarchical relationships
Best Practices:
- Focus on user intent over keyword density
- Maintain natural language flow
- Include both broad and specific terms
- Update maps regularly as topics evolve
Correct vs. Incorrect Implementation:
✅ Correct:
Topic: Digital Marketing
- Primary: “social media marketing”
- Related: “Facebook ads,” “Instagram strategy”
- Attributes: “engagement rates,” “audience targeting”
- Connected entities: “platform algorithms,” “content strategy”
❌ Incorrect:
Topic: Digital Marketing
- Disconnected terms: “website,” “computer,” “internet”
- Unrelated concepts: “office supplies,” “business cards”
- Missing hierarchy: random list of marketing terms
- No semantic connections between entities
2. Find LSI & Secondary Keywords Using Co-Occurrence and NLP Techniques
LSI (Latent Semantic Indexing) keywords are contextually related terms that search engines use to understand content depth and relevance. Secondary keywords are supporting phrases that reinforce the main topic while targeting additional search intent.
On-Page SEO Step-by-Step Process for finding LSI and secondary keywords.
1. Gather Primary Keywords
Export main keyword list from SEO tools like Ahrefs or SEMrush and group keywords by search intent and topic.
Example:
✅ Correct: “dog training” → “puppy obedience”, “positive reinforcement methods”
❌ Incorrect: “dog training” → “dog food”, “pet supplies” (unrelated context)
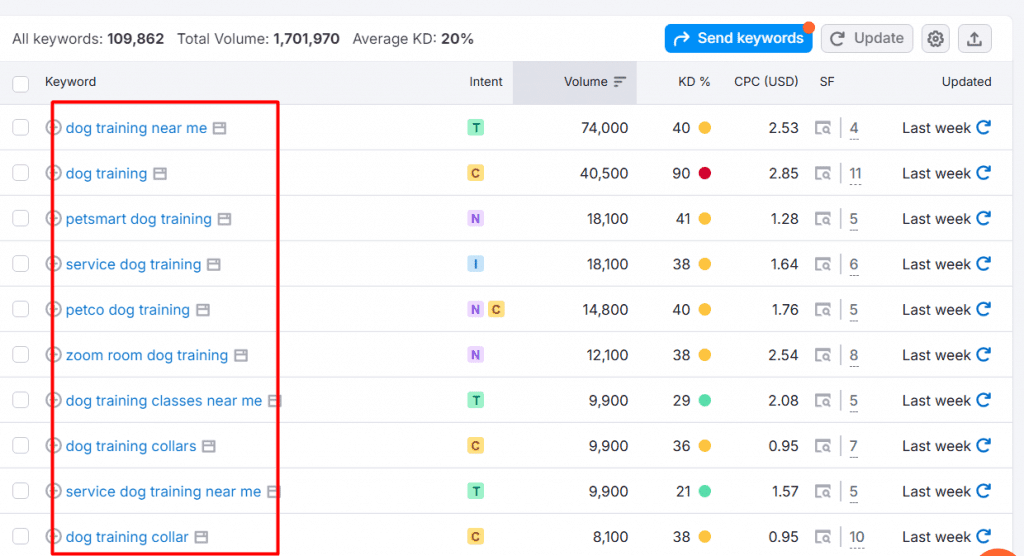
2. Analyze Top-Ranking Content
Review top 10 SERP results for primary keywords
Note recurring phrases and related terms
Document content structure and subtopics
Example:
✅ Correct: Study how competitors use terms like “behavioral training”, “command techniques”
❌ Incorrect: Copying competitor content verbatim
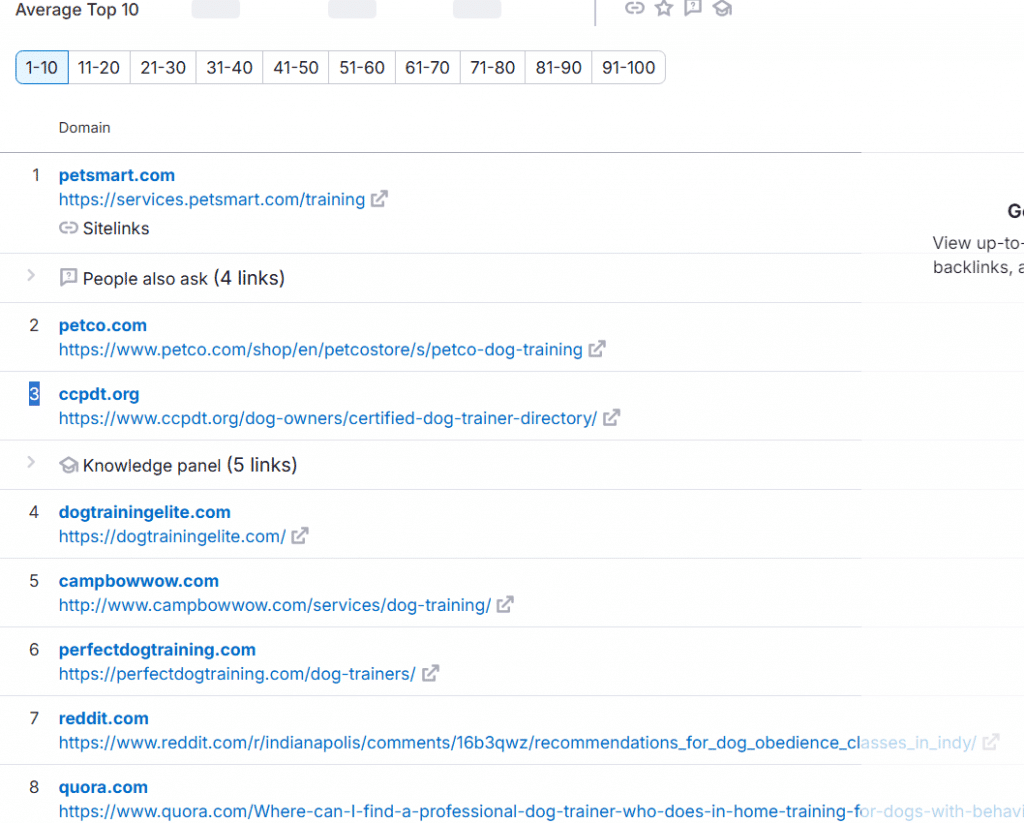
3. Use Keyword Clustering Tools
Input primary keywords into tools like Writerzen or CanIRank. I personally use Writerzen to generate clusters of semantically related terms by relevance and search volume.
Example:
✅ Correct: Creating topic clusters like “dog training” → “basic commands” → “sit” → “stay”
❌ Incorrect: Random keyword grouping without semantic connection

4. Implement Co-occurrence Analysis
Identify frequently paired terms in top content, map relationships between primary and secondary keywords, and document phrase patterns.
Example:
✅ Correct: “positive reinforcement” frequently appears with “reward-based training”
❌ Incorrect: Forcing unnatural keyword combinations
- Apply NLP Tools
Use Google’s Natural Language API to analyze entity relationships and extract relevant phrases and context.
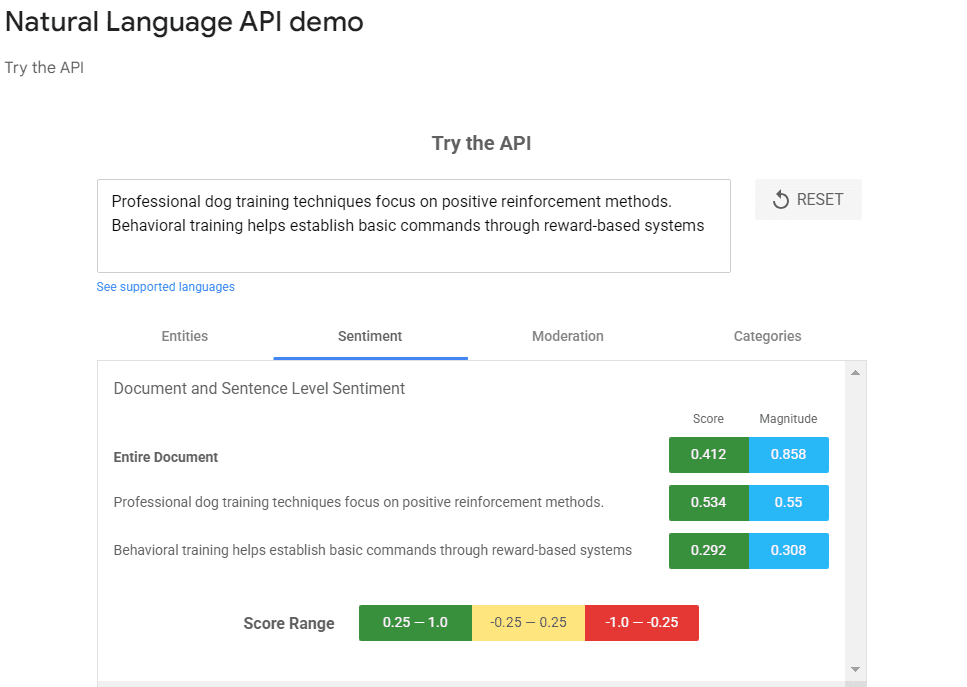
Example:
✅ Correct: Understanding that “canine behavior” relates to “dog psychology”
❌ Incorrect: Ignoring semantic relationships between terms
Best Practices:
- Maintain natural language flow
- Focus on user intent first
- Integrate keywords contextually
- Test different keyword combinations
- Monitor performance metrics
- Update content based on SERP changes
Example of writing sentence using focus keyword, LSI, and secondary keywords.
✅ Correct Implementation:
“Professional dog training techniques focus on positive reinforcement methods. Behavioral training helps establish basic commands through reward-based systems…”
❌ Incorrect Implementation:
“Dog training dog trainer puppy training obedience training dog behavior training…”
3. Craft an Engaging, Semantically Optimized SEO Title (Include Secondary Keywords)
Websites with optimized SEO titles increase click-through rates by 85% and boost overall website traffic.
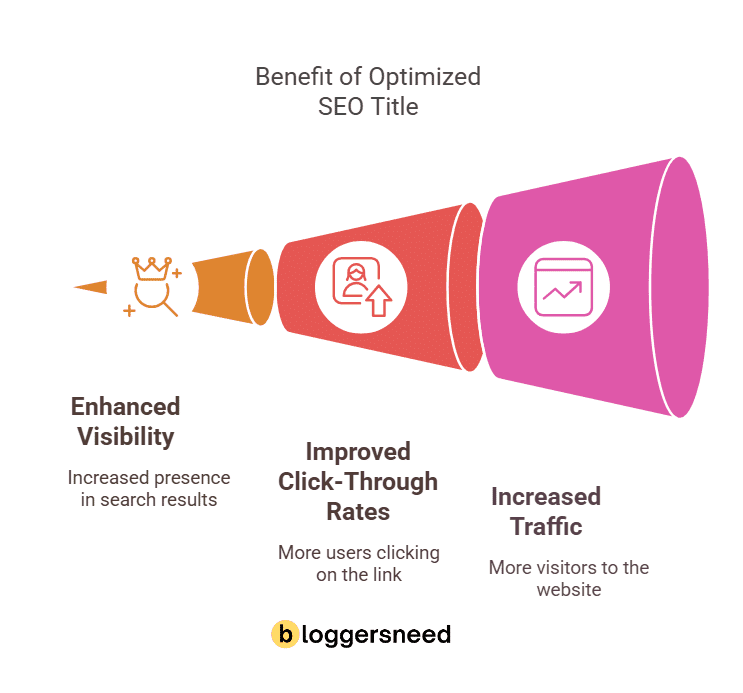
Crafting Semantically Optimized SEO Titles for On-Page SEO: A Step-by-Step Guide
Step 1: Define Target Keywords
Research primary keyword with highest search intent relevance. Identify 2-3 supporting secondary keywords. Example: Primary = “SEO titles”, Secondary = “optimization”, “click rates”
Step 2: Analyze Top-Ranking Competition
Study first page SERP titles. Note common patterns and formats. Document high-performing title structures.
Step 3: Structure Your Title
Place primary keyword within first 60 characters. Add secondary keywords naturally. Keep total length under 60-65 characters.
If you write about the topic ‘SEO title optimization’ then you should place the focus keyword in the beginning of the title followed by the secondary keyword.
Check this example to learn how to write an effective title for your article.
✅ Correct: “SEO Title Optimization: 7 Proven Strategies for Higher CTR”
❌ Incorrect: “The Best Ways to Make Amazing SEO Titles That Will Help Your Website Rank Better in Search”
Step 4: Incorporate Power Elements
Add numbers when applicable. Include year for freshness. Use emotional triggers.
✅ Correct: “15 SEO Title Formulas (2026): Triple Your Click-Through Rate”
❌ Incorrect: “Some Good Tips for Making SEO Titles”
Step 5: Test and Refine
Monitor CTR in Search Console. A/B test different variations. Track performance metrics. Adjust based on data.
Best Practices:
- Use brackets or parentheses for modifiers
- Include benefit-driven language
- Maintain natural readability
- Match search intent
- Avoid keyword stuffing
4. Write a Compelling Meta Description Incorporating LSI & Secondary Keywords
Writing Compelling Meta Descriptions with LSI Keywords
What is Meta Description?
A meta description is an HTML attribute that provides a concise summary of a webpage’s content, displayed in search results to influence click-through rates.
A meta description should be a concise summary of a webpage’s content, displayed in search results to influence click-through rates.
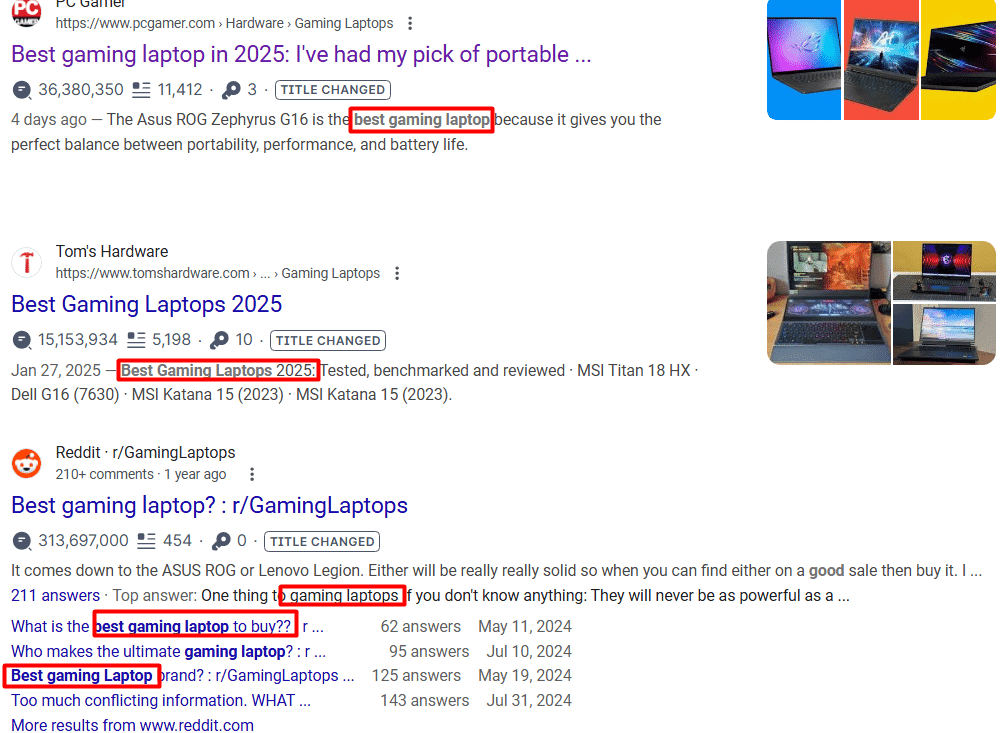
Effective On-Page SEO Tips for Writing SEO-Optimized Meta Descriptions for Your Articles
Step 1: Research Primary and LSI Keywords
- Identify your main keyword using tools like Google Keyword Planner
- Find semantic variations through Google’s “Related Searches”
- List 3-4 relevant secondary keywords that support your topic
Step 2: Structure Your Description
- Place primary keyword in first 50 characters
- Include 2-3 LSI keywords naturally
- Limit length to 155-160 characters
- Add compelling call-to-action
Step 3: Optimize for Click-Through
- Use action verbs (discover, learn, explore)
- Address user intent directly
- Highlight unique value proposition
- Include specific benefits or features
Step 4: Test and Refine
- Monitor click-through rates in Search Console
- A/B test different variations
- Update based on performance metrics
✅ Correct Example:
“Master SEO copywriting techniques: Learn proven content optimization strategies, keyword research methods, and writing tips to boost your organic traffic today.”
❌ Incorrect Example:
“SEO copywriting tips and tricks for better SEO and content optimization with keywords and good writing for better rankings in search engines today.”
5. Structure H1 and Subheadings With Semantic Keyword Variations
How to Structure Headings for SEO and User Experience
What is Heading Structure?
A heading structure is a hierarchical organization of content using HTML header tags (H1-H6) that guides both users and search engines through webpage content.
A heading structure serves two primary purposes: it helps users quickly understand the content and its organization, and it provides search engines with a clear hierarchy of content to improve search engine rankings.
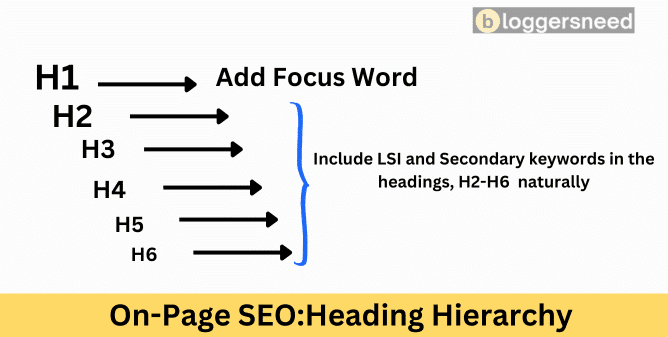
Step 1: Create a Single H1 Tag
- Place your primary keyword in the H1
- Keep it under 60 characters
- Make it unique for each page
✅ Correct: Ultimate Guide to Content Marketing
❌ Incorrect: Welcome to Our Website
Step 2: Organize Main Topics with H2 Tags
- Break content into logical sections
- Use relevant keyword variations
- Maintain natural language flow
✅ Correct: Content Strategy Development
❌ Incorrect: Strategy Development Content
Step 3: Add Supporting Subtopics with H3-H6
- Nest related concepts under parent headings
- Include LSI keywords naturally
- Maintain logical hierarchy
Step 4: Optimize Heading Keywords
- Use semantic variations
- Include long-tail keywords
- Maintain topical relevance
✅ Correct: “Content Marketing Strategy” → “Content Planning” → “Topic Research”
❌ Incorrect: “Marketing” → “Strategy” → “Content”
Step 5: Review Heading Structure
- Check heading levels flow properly
- Ensure no skipped levels
- Verify keyword distribution
✅ Correct: H1 → H2 → H3
❌ Incorrect: H1 → H3 → H2
6. Develop a Strong Introduction by Answering Primary Search Intent
A strong introduction is essential for effective On-page SEO, as it clearly establishes the primary intent of the content, aligns with user queries, and captivates the audience’s attention from the outset.
The steps below explain how to write a semantic SEO introduction for any topic.
Step 1: Analyze Search Intent
Review search queries and user patterns. Categorize intent type (informational, navigational, commercial, transactional). List common user questions related to your topic.
Step 2: Craft Direct Answer Opening (First 150-200 characters)
✅ Correct: “A mortgage down payment is the initial cash payment made when purchasing a home, typically 3-20% of the total purchase price.”
❌ Incorrect: “In this article, we’ll explore everything you need to know about mortgage down payments.”
Step 3: Structure Key Information
Place primary definition or answer first. Add essential statistics or data points. Include critical qualifications or exceptions.
Step 4: Incorporate Semantic Keywords
List main keyword variations. Map related terms and phrases. Natural placement within sentences.
Step 5: Add Supporting Context
Connect main answer to user needs. Provide immediate value proposition. Bridge to detailed content sections.
Step 6: Test Introduction Effectiveness
Verify direct answer appears in featured snippet format. Confirm primary keyword placement. Check readability and scannability.
Best Practices:
- Keep sentences concise and clear.
- Use active voice.
- Maintain natural language flow.
- Include relevant numbers or statistics.
- Answer secondary user questions.
- Avoid unnecessary background information.
7. Expand Content Depth Using Supporting Subtopics and Latent Queries
Expanding Content Depth Through Supporting Subtopics and Latent Queries
What is Content Depth Expansion?
Content depth expansion is the systematic process of enriching website content by identifying and integrating related subtopics, semantic variations, and user search patterns to create comprehensive, authoritative resources.
Steps:
- Conduct keyword research to identify primary and secondary topic clusters.
- Map out hierarchical relationships between main topics and subtopics.
- Analyze search intent patterns using tools like Google Search Console.
- Create a content outline incorporating identified subtopics.
- Develop detailed sections addressing each supporting concept.
- Implement internal linking between related content pieces.
- Optimize for semantic search terms and variations.
- Review and update content based on user engagement metrics.
Best Practices:
- Use topic modeling tools to identify content gaps.
- Structure content in logical hierarchies.
- Include relevant examples and case studies.
- Address common user questions proactively.
- Maintain consistent terminology across related content.
- Update content regularly with new supporting information.
- Track performance metrics for each content cluster.
Correct vs. Incorrect Implementation:
✅ Correct:
- Main topic: Coffee Brewing
- Subtopic 1: Water Temperature (195-205°F)
- Subtopic 2: Grind Size (coarse for French press)
- Subtopic 3: Brewing Time (4-5 minutes)
Internal links connect related articles
Search intent matches user queries
❌ Incorrect:
- Main topic: Coffee Brewing
- Random unrelated subtopics
- No supporting data or examples
- Missing key information
- No internal linking structure
- Ignores user search patterns
8. Integrate LSI & Secondary Keywords Naturally Throughout the Content
Natural LSI & Secondary Keyword Integration: A Step-by-Step Guide
What is LSI Keywords?
LSI (Latent Semantic Indexing) keywords are conceptually related terms that search engines use to determine content relevance and depth. Secondary keywords are supporting search terms that enhance topical authority.
On-page SEO Steps for Integrating LSI Keywords in Content:
- Research Related Terms
Use tools like Google’s “People Also Ask” and “Related Searches”
Analyze competitor content for common semantic patterns
Create clusters of thematically connected phrases - Map Content Structure
Outline main sections and subtopics
Assign relevant LSI terms to each section
Plan secondary keyword placement points - Optimize Key Elements
Title: Include primary keyword
H1-H6: Incorporate LSI variations
Meta description: Use natural keyword combinations
First paragraph: Place main concept and key LSI term
Write Natural Content
✅ Correct: “Digital marketing strategies encompass social media promotion, content optimization, and targeted advertising.”
❌ Incorrect: “Digital marketing strategies digital marketing tips digital marketing solutions for business growth.”
- Strategic Placement
Insert LSI terms in topic transitions
Use secondary keywords in supporting examples
Include related terms in conclusion paragraphs
Best Practices:
- Maintain 2-3% keyword density
- Prioritize readability over keyword placement
- Vary phrase structures and word forms
- Test content with target audience members
- Monitor search performance and adjust accordingly
9. Use Bold, Italics, and Lists to Improve Content Scanability and NLP Parsing
Content Formatting Guide for Readability & NLP
What is Content Formatting?
Content formatting refers to the strategic use of visual elements and text structures to optimize both human readability and machine comprehension of digital content.
Steps for Effective Content Formatting:
- Apply Header Hierarchy: Use H1 for main title. Structure subtopics with H2-H6. Maintain logical nesting order.
- Implement Strategic Emphasis: Bold primary keywords and key concepts. Italicize supporting terms and definitions. Avoid over-formatting to maintain impact.
- Structure Information Flow: Break content into digestible paragraphs. Maintain consistent spacing. Use transition sentences between sections.
Breakdown:
Break content into smaller sections to improve flow. This helps readers navigate the content more easily.
Maintain Consistency:
Maintain consistent spacing between paragraphs and sections. This improves the overall readability of the content.
- Create Organized Lists: Use bullet points for related items. Apply numbers for sequential steps. Keep list items parallel in structure.
Best Practices:
- Limit formatting to 1-2 elements per paragraph.
- Ensure consistent formatting patterns.
- Maintain clear visual hierarchy.
- Include white space for readability.
Correct vs. Incorrect Implementation:
✅ Correct:
- Key concept with supporting definition.
- Clean, structured lists.
- Consistent heading levels.
❌ Incorrect:
- Random mixed formatting.
- Dense, unbroken paragraphs.
- Skipped heading levels.
10. Embed Internal Links Contextually to Reinforce Topical Authority
A Step-by-Step Guide to Embedding Internal Links Contextually
What is Internal Linking?
Contextual internal linking is the practice of connecting related pages within your website using relevant anchor text that naturally integrates with the surrounding content while reinforcing topical relationships.
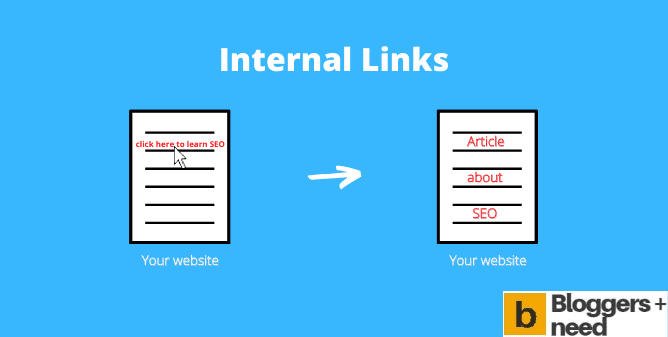
Internal linking steps for on-page SEO.
- Identify key pages to link: Map out your site’s content structure. List priority pages that need link authority. Note related topics and supporting content.
- Select natural placement points: Review content for topical mentions. Focus on the first 300 words. Look for explanatory sections where links add value.
- Craft descriptive anchor text: Use keywords naturally describing destination content. Keep anchor text between 2-6 words. Ensure text flows within the sentence.
- Balance link distribution: Add 2-3 internal links per 500 words. Space links evenly throughout content. Vary anchor text for similar destination pages.
Best Practices:
- Link to hierarchically relevant pages
- Maintain consistent internal linking patterns
- Update old content with new relevant links
- Remove or fix broken internal links
Correct vs. Incorrect Examples:
✅ Correct: “Our comprehensive SEO audit process reveals technical issues affecting site performance.”
❌ Incorrect: “Click here to learn about SEO audits” or “Read more about audits here”
✅ Correct: “Implementing structured data markup improves search visibility for product pages.”
❌ Incorrect: “Go to this page to learn about structured data” or “See more >”
11. Include Relevant Images, Videos, and Infographics for Engagement
How to Include Multimedia Elements for Maximum Engagement
What is Multimedia Integration?
Multimedia integration is the strategic placement of images, videos, and infographics within content to increase user engagement, improve information retention, and enhance visual appeal.
Step-by-Step Implementation:
1. Assess Content Requirements
- Review your text content
- Identify key points that need visual support
- Determine appropriate multimedia types for each section
2. Select High-Quality Visuals
- Choose relevant stock photos or create custom images
- Ensure resolution meets platform requirements
- Verify copyright permissions and licensing
3. Optimize Multimedia Elements
- Resize images to recommended ratios (1:1, 4:3, 16:9)
- Compress videos to under 100MB
- Scale infographics to 800px maximum width
- Add descriptive alt text (125 characters max)
4. Position Elements Strategically
- Place visuals near related text
- Break up long text sections
- Maintain consistent spacing
- Ensure mobile responsiveness
Best On-Page SEO Practices for Images
- Use original, high-quality visuals
- Maintain consistent branding
- Include captions for context
- Test loading speeds
- Implement lazy loading for better performance
Correct vs. Incorrect Implementation:
✅ Correct:
✓ Relevant product image beside description
✓ Compressed video with preview thumbnail
✓ Mobile-responsive infographic
✓ Descriptive alt text: “Chart showing 94% engagement increase with multimedia content”
❌ Incorrect:
✗ Generic stock photos unrelated to content
✗ Oversized videos causing slow loading
✗ Stretched or distorted images
✗ Missing or vague alt text: “graph1.jpg”
12. Write Descriptive and Keyword-Rich Alt Text for Images (Use LSI Keywords)
How to Write Descriptive and Keyword-Rich Alt Text for Images
What is Alt Text?
Alt text (alternative text) is an HTML attribute that provides a text description of an image, serving both search engines and visually impaired users while incorporating semantically related keywords for better context and discoverability.

A Step-by-Step Guide to Writing SEO-Optimized Image Alt Text
1. Analyze the image content
- Identify the main subject
- Note key visual elements
- Determine the image’s purpose within the content
2. Write a clear description
- Use natural language
- Keep text under 125 characters
- Focus on essential details
- Include relevant context
3. Incorporate target keywords
- Place primary keyword naturally within description
- Add LSI keywords where appropriate
- Maintain readability
4. Review and optimize
- Check for accuracy
- Verify character length
- Ensure natural flow
- Test with screen readers
Best Practices:
- Be specific and descriptive
- Avoid keyword stuffing
- Include action words when relevant
- Match image context to surrounding content
- Use proper grammar and punctuation
Examples:
✅ Correct Implementation:
“Red Ferrari F40 supercar racing on mountain road at sunset”
“Fresh organic strawberries in wooden basket at farmers market”
“Professional woman delivering business presentation to diverse team”
❌ Incorrect Implementation:
“car img123.jpg”
“strawberry, fruit, food, fresh, organic, healthy eating, nutrition”
“business meeting office corporate professional workplace team building”
13. Embed Videos With Transcripts for Improved Entity Indexing
Video Transcript Implementation for Entity Indexing
What is Video Transcription?
A process of adding searchable text versions of video content to help search engines better understand, index, and rank multimedia content through entity recognition.
Step 1: Create Accurate Video Transcripts
- Use professional transcription services or AI tools like Rev, Otter.ai
- Include speaker identification and timestamps
- Review and edit for accuracy
✅ Correct: [00:01:15] Dr. Smith: The Mars rover discovered traces of water in Jezero Crater.
Incorrect: Speaker1: The robot found some stuff on Mars.
Step 2: Format Transcripts Properly
- Save in multiple formats (SRT, VTT, plain text)
- Structure with proper timing marks
- Include punctuation and capitalization
✅ Correct:
1
00:00:00,000 –> 00:00:03,000
Welcome to our guide on quantum computing.
Incorrect:
welcome to our guide on quantum computing
Step 3: Implement Schema.org Markup
- Add VideoObject structured data
- Include transcript URL and content
- Link to related entities
✅ Correct:
{
“@type”: “VideoObject”,
“transcript”: “Dr. Smith discusses Mars exploration…”,
“name”: “Mars Rover Discovery”
}
❌ Incorrect:
{
“video”: “Mars video”,
“text”: “About Mars”
}
Step 4: Optimize Transcript Placement
- Position transcript below or beside video
- Add collapsible transcript sections
- Include jump-to timestamp links
Step 5: Test and Monitor
- Verify transcript accuracy
- Check schema validation
- Monitor search console performance
- Track entity recognition in search results
Best Practices:
- Maintain consistent formatting
- Update transcripts when video content changes
- Include relevant keywords naturally
- Cross-reference entities with authoritative sources
- Use descriptive timestamps
- Implement proper HTML5 semantic markup
14. Leverage Schema Markup (Article, FAQPage, VideoObject) for Better Indexing
What is Schema Markup?
Schema markup is structured data code added to websites that helps search engines understand content context and relationships, enabling rich snippets in search results.
WordPress SEO plugins like RankMath and Yoast SEO allow you to add various schema types to blog posts.
Steps to Implement Key Schema Types:
1. Article Schema Implementation
Select appropriate Article type (NewsArticle, BlogPosting, etc.). Add core required properties:
- headline
- author
- datePublished
- publisher
To effectively implement on-page SEO for article schema markup, prioritize including optional properties such as images and descriptions to enhance clarity and contextual relevance.
2. FAQPage Schema Setup
Structure Q&A content in proper format. Add FAQPage wrapper. Include individual Question and Answer pairs. Ensure each Q&A pair contains:
- question property
- answer property
- VideoObject Schema Integration
Identify video content requiring markup. Include essential properties:
- name
- description
- thumbnailUrl
- uploadDate
- duration
Add optional properties like transcript or caption.
Best Practices:
- Test implementation using Google’s Rich Results Testing Tool
- Use JSON-LD format (preferred by Google)
- Maintain consistency across similar content types
- Update schema when content changes
- Avoid markup on hidden content
Correct vs. Incorrect Implementation:
✅ Correct Article Schema:
”’json
{
“@type”: “NewsArticle”,
“headline”: “New Study Reveals…”,
“author”: “John Smith”,
“datePublished”: “2023-10-15”,
“publisher”: {
“@type”: “Organization”,
“name”: “Example News”
}
}
”’
❌ Incorrect Article Schema:
”’json
{
“@type”: “Article”,
“title”: “New Study Reveals…”,
“writer”: “John Smith”,
“date”: “October 15, 2023”
}
”’
How to validate schema code?
- Copy schema code
- Open Rich Results Testing Tool
- Paste code and analyze
- Fix any reported errors
- Retest until validation passes
15. Improve URL Structures for Clarity and Keyword Relevance (Use Secondary Keyword)
URL Structure Optimization Guide
What is URL Structure?
URL structure represents the hierarchical organization of web addresses using clear, keyword-relevant paths that help both users and search engines understand content organization and relevance.
On-Page SEO Steps to Improve URL Structures:
1. Create a logical hierarchy
- Define main categories
- Group related content into subcategories
- Structure: domain.com/category/subcategory/page-name
2. Format URLs properly
- Use lowercase letters
- Replace spaces with hyphens
- Remove special characters
- Limit URL length to 50-60 characters
3. Incorporate keywords strategically
Place primary keyword near the beginning
Include secondary keyword naturally
Remove unnecessary stop words
4. Implement consistent naming conventions
- Use clear, descriptive terms
- Maintain consistent category names
- Apply uniform formatting rules
Best Practices:
- Keep URLs short and meaningful
- Use readable words, not numbers or codes
- Avoid parameter strings when possible
- Include target keywords without stuffing
- Maintain a logical content hierarchy
Correct vs. Incorrect Examples:
✅ Correct: domain.com/digital-marketing/seo/url-optimization-guide
❌ Incorrect: domain.com/p=123?id=456&category=dm&subcat=seo
domain.com/digital-marketing/search-engine-optimization/complete-guide-to-url-structure-optimization-2023
✅ Correct: domain.com/cameras/mirrorless/sony-a7iii-review
❌ Incorrect: domain.com/products/the-complete-and-detailed-review-of-the-sony-a7iii-mirrorless-camera
17. Optimize Page Speed by Compressing Images & Reducing Heavy Scripts
Page Speed Optimization: A Technical Guide to Image Compression and Script Reduction
What is Page Speed Optimization?
Page speed optimization refers to the systematic process of reducing webpage load times by minimizing file sizes and optimizing delivery methods for images and scripts.
At BloggersNeed, we use WP Rocket and Permatters, two of the best cache plugins, to speed up our website.
Below are the speed test results from this website’s Google PageSpeed Insights report.
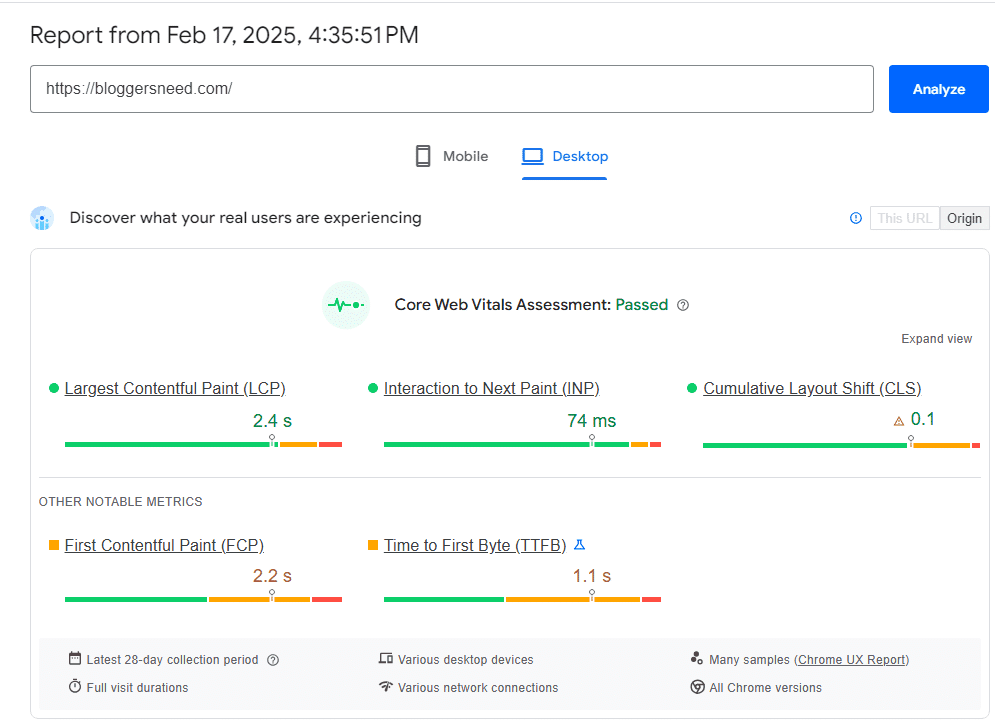
Step-by-Step Implementation:
1. Image Compression
- Install image optimization tools (TinyPNG, ImageOptim, or Squoosh).
- Audit current image sizes using browser developer tools.
- Compress all images to below 100KB where possible.
- Convert images to next-gen formats (WebP, AVIF).
- Implement responsive image sizing using srcset attribute.
2. Script Optimization
- Remove unused JavaScript and CSS.
- Minify remaining code files.
- Defer non-critical JavaScript.
- Combine multiple CSS/JS files into single files.
- Enable browser caching via .htaccess.
3. Technical Implementation
- Enable GZIP compression.
- Configure lazy loading for below-fold images.
- Set up a CDN integration.
- Eliminate render-blocking resources.
- Implement critical CSS delivery.
Best Practices:
- Maintain image aspect ratios.
- Keep individual file sizes under 200KB.
- Use async loading for non-essential scripts.
- Regular performance monitoring using GTmetrix.
- Mobile-first optimization approach.
Expected Outcomes:
- 40-70% reduction in image file sizes.
- Sub-3-second page load times.
- Improved mobile performance scores.
- Higher search engine rankings.
- Reduced bounce rates.
18. Enhance Mobile Usability and Core Web Vitals Performance
How to Enhance Mobile Usability and Core Web Vitals Performance
What Are Core Web Vitals?
Core Web Vitals are Google’s metrics for measuring user experience, focusing on loading performance (LCP), interactivity (FID), and visual stability (CLS) on mobile devices.

Step 1: Measure Current Performance
Run Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test
Use PageSpeed Insights to check Core Web Vitals scores
Document baseline metrics for comparison
Step 2: Optimize Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
✅ Correct: Compress images, use CDN, implement lazy loading
❌ Incorrect: Loading full-size images, multiple server requests
Step 3: Improve First Input Delay (FID)
✅ Correct: Minimize JavaScript, remove unused code, defer non-critical scripts
❌ Incorrect: Loading all scripts at once, heavy JavaScript frameworks
Step 4: Minimize Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
✅ Correct: Set image dimensions, reserve space for ads, use stable fonts
❌ Incorrect: Dynamic content without reserved space, unstable layouts
Step 5: Implement Mobile Responsiveness
Add viewport meta tag:
Use fluid grids and flexible images
Apply media queries for breakpoints
Best Practices:
1. Target metrics
- LCP: Under 2.5 seconds
- FID: Under 100 milliseconds
- CLS: Below 0.1
2. Mobile-specific considerations
- Minimum touch target size: 48×48 pixels
- Readable font size: 16px minimum
- Adequate spacing between interactive elements
3. Regular testing and monitoring
- Monthly performance audits
- A/B testing of optimizations
- Continuous monitoring via Google Search Console
19. Reduce Unnecessary JavaScript & Bloated DOM Elements
Reducing Unnecessary JavaScript & Bloated DOM Elements: A Technical Guide
What is Code Optimizing?
Code optimization process that removes redundant JavaScript code and excessive DOM elements to improve website performance, reduce load times, and minimize server processing.
Step-by-Step Implementation:
- Audit JavaScript Code
Run performance profiler in Chrome DevTools. List all JavaScript files and functions. Identify unused or duplicate code. Document dependencies between functions. - Minimize JavaScript
Remove unused functions and variables. Combine multiple .js files into single file. Convert synchronous loads to async where possible. - Clean DOM Structure
Remove nested div containers. Delete empty elements. Replace inline styles with CSS classes. - Implement Lazy Loading
Add loading=”lazy” to images below fold. Defer non-critical scripts. Use IntersectionObserver for dynamic content. - Optimize Remaining Code
Minify JavaScript files. Compress assets. Enable browser caching.
Example:
❌ function calculateTotal(price, tax) {
return price + (price * tax);
}
✅ const calcTotal=(p,t)=>p+p*t;
Best Practices:
Use code splitting for large applications. Implement tree shaking. Set performance budgets. Regular performance monitoring. Document code dependencies. Maintain clean code architecture.
Performance Metrics:
Aim for <2s initial page load. Reduce JavaScript bundle size by 40%. Maintain DOM depth under 15 levels. Keep total DOM elements under 1500.
20. Monitor Dwell Time, Bounce Rate, and Scroll Depth to Analyze User Engagement
How to Monitor User Engagement Metrics
What is User Engagement Metrics?
User engagement metrics measure how visitors interact with website content through dwell time (time spent on page), bounce rate (percentage of single-page visits), and scroll depth (scrolling distance).
Steps:
1. Set up tracking tools
- Install Google Analytics
- Implement heatmap software (e.g., Hotjar, CrazyEgg)
- Configure scroll depth triggers
2. Establish baseline metrics
- Record current dwell time averages
- Document existing bounce rates
- Measure typical scroll depths
3. Define target thresholds
- Dwell time: 3+ minutes
- Bounce rate: Below 65%
- Scroll depth: 75% or higher
3. Monitor metrics regularly
- Check weekly analytics reports
- Review heatmap data monthly
- Track trend changes quarterly
4. Analyze performance
- Compare metrics against benchmarks
- Identify high/low performing pages
- Document patterns and anomalies
Best Practices:
- Segment data by traffic source
- Compare desktop vs. mobile metrics
- Create custom dashboards for quick analysis
- Set up automated alerts for significant changes
Correct vs. Incorrect Implementation:
✅ Correct:
- Regular monitoring schedule
- Data-driven content adjustments
- Segmented analysis by page type
- Multi-tool verification
❌ Incorrect:
- Sporadic data checking
- Ignoring mobile metrics
- Using single data source
- No baseline comparisons
21. Track Content Performance Using Predictive SEO Models & Behavioral Analytics
Track Content Performance Using Predictive SEO Models & Behavioral Analytics
What is Predictive SEO Modelling?
Predictive SEO modeling combines historical performance data and user behavior metrics to forecast content success and guide optimization decisions through data-driven insights
Steps:
- Set up analytics tracking
Install Google Analytics and Search Console
Configure goal tracking and event monitoring
Implement heat mapping tools like Hotjar or Crazy Egg - Collect baseline performance data
Track organic traffic trends
Monitor click-through rates (CTR)
Measure average time on page
Record bounce rates and exit pages
Document conversion rates - Analyze behavioral patterns
Review user flow diagrams
Study scroll depth metrics
Examine interaction heat maps
Assess page navigation paths - Build predictive models
Identify correlations between metrics
Create performance benchmarks
Develop forecasting formulas
Set performance thresholds - Implement optimization tests
Design A/B tests based on data insights
Test content variations systematically
Monitor impact on key metrics
Document successful changes
Best Practices:
- Update tracking codes regularly
- Clean data sets monthly
- Focus on statistically significant patterns
- Test one variable at a time
- Document all optimization changes
Correct vs. Incorrect Implementation:
✅ Correct:
- Using structured data collection methods
- Testing hypotheses with control groups
- Making data-backed optimization decisions
- Regular monitoring and adjustment cycles
❌ Incorrect:
- Random content changes without data
- Ignoring user behavior patterns
- Skipping control group testing
- Implementing multiple changes simultaneously
FAQs About On-Page SEO
Can I Rank My Website Using Only On-Page SEO?
While strong on-page SEO can significantly improve your rankings, it is generally not sufficient on its own. A combination of both on-page and off-page SEO strategies is typically necessary for optimal performance in search engine results.
Is Technical SEO Part of On-Page SEO?
Yes, technical SEO is a subset of on-page SEO. It involves optimizing the technical aspects of a website, such as site speed, mobile-friendliness, indexing, and crawlability, to enhance user experience and search engine visibility.
Is Link Building Part of On-Page SEO?
No, link building is considered part of off-page SEO. It involves acquiring backlinks from other websites to enhance the authority and visibility of a site, while on-page SEO focuses on optimizing elements within the website itself, such as content and meta tags.
Is Social Bookmarking Useful for On-Page SEO?
Social bookmarking is primarily an off-page SEO tactic. While it can drive traffic and increase visibility, it does not directly influence the on-page SEO factors that affect how search engines rank a website.
Does Keyword Density Help On-Page SEO?
Keyword density can have some impact on on-page SEO; however, it is no longer a primary ranking factor. Modern SEO practices emphasize the importance of content quality and relevance over strict keyword usage.
What Is a Good On-Page SEO Score?
A good on-page SEO score typically ranges from 80 to 100%, depending on the specific tools used for evaluation. However, achieving a high score does not guarantee top rankings; it should be part of a broader SEO strategy.
Is There a Tool to Do On-Page SEO?
Yes, there are numerous tools available for on-page SEO analysis, including Page Optimizer Pro, Surfer SEO, and Cora SEO Software. These tools can help evaluate various aspects of your website’s optimization and provide actionable insights for improvement.
What is OFF-Page SEO?
Off-page SEO refers to optimization activities performed outside your website to improve search engine rankings and online visibility through backlinks, social signals, and brand mentions.
Steps to Implement Off-Page SEO:
1. Build Quality Backlinks
Identify authoritative websites in your niche. Create valuable content worthy of linking. Reach out to website owners with personalized pitches. Monitor backlink profile using tools like Ahrefs or Moz.
2. Optimize Social Media Presence
Create profiles on relevant platforms. Share website content consistently. Engage with followers and industry leaders. Track social media metrics.
3. Generate Brand Mentions
Submit guest posts on industry blogs. Participate in interviews and podcasts. Create shareable infographics and studies. Engage in community discussions.
Best Practices:
✓ Focus on relevant, high-authority websites
✓ Maintain natural link velocity
✓ Diversify anchor text
✓ Create shareable, valuable content
✓ Build genuine relationships with industry peers
Correct vs. Incorrect Implementation:
✅ Correct:
- Earning backlinks through valuable content
- Building relationships with industry leaders
- Creating diverse, natural anchor text
- Engaging authentically on social media
❌ Incorrect:
- Buying links from link farms
- Spamming comment sections
- Using exact-match anchor text repeatedly
- Automating social media engagement
Affiliate Disclosure: Some of the links in this post are affiliate links, which means I may earn a small commission if you make a purchase through those links. This comes at no extra cost to you. Thank you for your support!
